Omega- 3, 6 and 9 Benefits for Brain Health
In a world jam-packed with biohacking solutions, it comes as no surprise that we are constantly looking for ways to optimize our brain health and function. However, it’s not necessarily all about biohacks. Simply eating a balanced and healthy diet goes a long way. In fact, omega-3s play a major role in preventing cognitive decline. So, let’s dig a little deeper into how omega-3s and brain health are intricately linked.
If you want to age gracefully with a sharp mind, you’ll want to keep reading. We’ve got some facts you won’t want to miss. We’ll also explore omega-3, omega-6—and omega-9, the benefits of each, the risks associated with an omega deficiency, and more.
What is the Difference Between Omega-3, Omega-6, and Omega-9?
Omega-3s are essential fatty acids that must be obtained through the food you eat. They include alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). Omega-6 fatty acids, on the other hand, include arachidonic and linoleic acids. Both omega-3s and 6s are polyunsaturated fats.
Meanwhile, omega-9 is a monounsaturated fat. This fatty acid can be made within the body, which means it’s a non-essential fatty acid and doesn’t have to be obtained through your diet.
Usually, it’s recommended to have the optimal omega-3-6-9 ratio be 2:1:1. Some experts even go so far as to recommend an omega-3 to 6 ratio between 2:1 and 4:1. However, this may come down to individual needs and what makes you feel your best. Often, it’s wise to start with a lower amount and slowly build up your dosage if needed.
Sources of Omega-3, 6, and 9
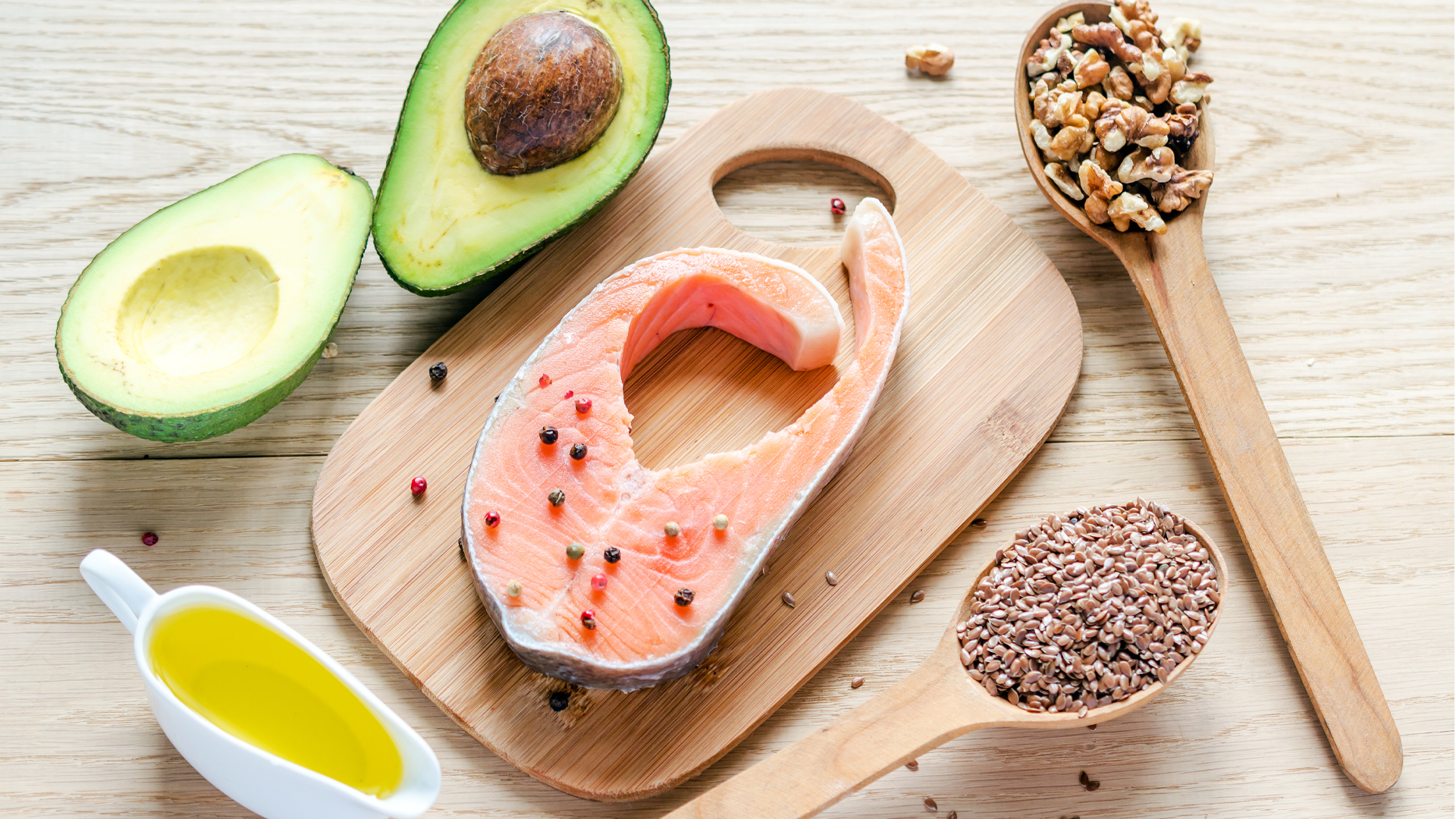
There are many natural sources of omega-3, 6, and 9, many of which have a reputation for being rich, satiating, and delicious. You can eat any of these foods alone, or combine them to create satisfying, omega-rich meals.
Food that includes omega-3:
- Oily fish:
- Salmon
- Mackerel
- Sardines
- Tuna
- Trout
- Nuts and seeds:
- Flax
- Chia
- Walnuts
- Green, leafy vegetables:
- Kale
- Spinach
- Avocados
Food that includes omega-6:
- Plant-based oils:
- Safflower
- Sunflower
- Soybean
- Corn
- Cotton seed
- Grapeseed
- Nuts and seeds:
- Almonds
- Walnuts
- Brazil nuts
- Cashews
- Avocados
Food that includes omega-9:
- Animal proteins:
- Beef
- Chicken
- Pork
- Cheese
- Milk
- Eggs
- Nuts and seeds:
- Sunflower
- Hazelnuts
- Macadamia nuts
- Pecans
- Pine nuts
- Fatty fruits:
- Avocados
- Olives
The Benefits of Omega-3
Omega-3 fatty acids are polyunsaturated fats. Most commonly found in fish, nuts, and seeds, this nutrient has various benefits, including:
- Reducing your risk of depression and anxiety.
- Improving eye health.
- Promoting early brain health and development (Studies show it reduces developmental delays, behavioral problems, and the risk of cerebral palsy, autism, and ADHD.)
- Adequate consumption of omega-3s during pregnancy also contributes to improved communication and social skills of the baby, as well as potentially a higher intelligence.
- Improving heart health.
- Reducing inflammation.
- Reducing relapses and other symptoms in individuals with bipolar disorder and other psychiatric disorders.
- Decreasing the risk of age-related mental decline and Alzheimer’s Disease.
- Lowering the risk of childhood asthma.
- Reducing liver fat in those with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
- Improving bone strength.
- Increasing amount of quality sleep.
Undeniably, there is great importance when it comes to ensuring you get enough omega-3s in your diet. Yet, what happens when you don’t get enough?
The Benefits of Omega-6
Omega-6 fatty acids are polyunsaturated fats, similar to omega-3s. However, omega-6s have a slightly different molecular structure and is used mainly for energy.
Other benefits of omega-6 fatty acids include:
- Reduce and prevent nerve pain
- Regulate blood pressure
- Improve bone health
- Reduced risk of heart disease
- Manage ADHD symptoms
- Regulate inflammation
- Improves kidney, lung, and blood vessel functions
- Essential to cell membrane structure and function
The Benefits of Omega-9
Omega-9 fatty acids—also known as oleic acid—are monounsaturated fats produced in the body. Though it’s not as essential to a healthy diet as 3 or 6, it does play a key role in certain bodily processes, including:
- Brain development (It may boost memory and slow progression in certain memory-related conditions)
- Reduced risk of cardiovascular disease (raises HDL cholesterol and lowers LDL)
Omega Deficiency Symptoms and Risks
An omega-3 deficiency can arise from not eating enough omega-3 foods, such as fish or shellfish. When it comes to Omega-6s, many people tend to get too much in their diet through the consumption of various cooking oils. Yet, as mentioned above, you’re actually supposed to get twice as many omega-3s.
So, how do you know if you have an omega-3 deficiency? Some of the most common symptoms include:
- Dry skin
- Depression
- Dry eyes
- Joint pain
- Hair loss or hair thinning
- Poor circulation
- Heart issues
- Fatigue
Additionally, an omega-3 deficiency can increase your risk of heart disease, joint issues such as arthritis, allergies, mental health problems, and even neurodegenerative disorders such as dementia and memory loss.
The Best Ways to Increase Omega 3 Levels
As with most nutrients, the best way to increase your omega-3 levels is by eating more food containing omega-3. Some examples include:
- Salmon
- Mackerel
- Tuna
- Flaxseeds
- Chia seeds
- Walnuts
- Canola oil
- Flaxseed oil
Usually, it’s recommended to eat about eight ounces of fish a week to obtain adequate omega-3s.
If these aren’t readily available to you, you might find it easier to supplement omega-3s. There are a variety of options available online or at your local pharmacy or grocery store. You can also purchase supplements with all three omega fatty acids, including adequate ratios.
At the same time, you need to be careful regarding omega-3 consumption due to heavy metal toxicity in some supplement brands. Additionally, omega-3 supplementation is not suitable for individuals taking blood clotting medication due to potential interactions. Further, some experts warn against over-supplementing and encourage obtaining as many nutrients as you can from food.
Is Heavy Metal Toxicity an Issue When Taking Omega 3?
Heavy metal toxicity is an issue with some omega-3 supplement brands. This is why it always pays to do your due diligence and research any product before buying. Fish oils containing omega-3s might include mercury, lead, cadmium, and arsenic. Generally, this means you need to find a supplement that has been purified and tested to avoid these toxins.
Some of the best sources of heavy metal-free omega-3 supplements include:
The above supplements have been tested and purified, claiming to be free from any heavy metals or toxins which make them an ideal choice compared to other options on the market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Are you still searching for answers to your questions regarding omega-3s for brain health? Check out our frequently asked questions below for more information.
How long does it take for omega-3 to improve brain health?
When taking omega-3 for brain health, you can expect it to take about a month before they enter your brain cells. At the same time, the effects are cumulative over a person’s lifetime. This means that it’s best to include omega-3 in your diet or as supplements throughout your life so that decades down the road, you can continue to enjoy your life in the best health possible.
The University of Wisconsin further states that noticeable effects, such as mood or pain level improvements, from taking omega-3s can be expected within six weeks to six months.
How much omega-3 should I take for brain health?
This depends on your age and other factors. However, it’s often recommended to take about 1000 to 2000 mg of fish oil containing omega-3 for brain health, without exceeding a dose of 3000 mg.
Does omega-3 help with memory?
Yes! Omega-3 supports brain function and development, which includes helping to improve thinking and memory processes. Research even shows the positive effects omega-3 has on older adults’ memory function when compared to a placebo.
When should omega-3 be taken?
Generally, it doesn’t matter exactly when you take them. However, for optimal absorption, you’ll want to consume omega-3 supplements with food, such as part of a meal or snack. If you’re consuming omega-3 by eating fish or other whole foods, you don’t need to worry about the timing or the “how” as much.

Disclaimer: The statements made in this article have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. Any products or treatments mentioned are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. Please consult a licensed medical practitioner for medical advice.
At Innovative Medicine, we believe in transparency. We want you to know that we may participate in affiliate advertising programs pertaining to products mentioned herein.
See how we can help you restore complete health of body, mind & spirit.
Join our mailing list and receive exclusive offers + information!






Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!